Hyperopia, or farsightedness, is a common vision problem, affecting about a fourth of the population. People with hyperopia can see distant objects very well, but have difficulty focusing on objects that are up close. The condition is sometimes referred to as "hypermetropia" rather than hyperopia.
Farsighted people sometimes have headaches or eye strain and may squint or feel fatigued when performing work at close range. If you get these symptoms while wearing your eyeglasses or contact lenses, you may need an eye exam and a new prescription.
What Causes Hyperopia/Hypermetropia?
This vision problem occurs when light rays entering the eye focus behind the retina, rather than directly on it. The eyeball of a farsighted person is shorter than normal.
Please click here to watch a video about hyperopia, also called farsightedness.
In hyperopia, the eyeball is too short for the power of the cornea and lens, and light fails to come to a focus on the retina.
Many children are born farsighted, and some of them "outgrow" it as the eyeball lengthens with normal growth.
Sometimes people confuse hyperopia with presbyopia, which also causes near vision problems but for different reasons.
How Hyperopia affects vision
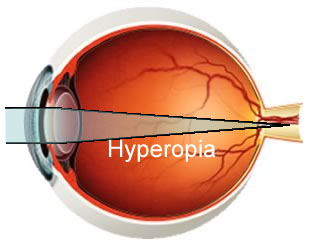 Farsightedness occurs when light entering the eye is focused behind the retina instead of directly on it . This is caused by an eye that is too short, whose cornea is not curved enough, or whose lens sits farther back in the eye than normal.
Farsightedness occurs when light entering the eye is focused behind the retina instead of directly on it . This is caused by an eye that is too short, whose cornea is not curved enough, or whose lens sits farther back in the eye than normal.
People who are farsighted see things at a distance more easily than they see things up close. If you are very farsighted, close objects may be so blurry that you can't do tasks such as reading or sewing. A farsighted eye sees things differently than an eye that is not farsighted.
Farsightedness (hyperopia) is usually a variation from normal, not a disease. How it affects you will likely change as you age.
How is the vision with Farsightedness
Diagnosing Farsightedness.
It’s easy to diagnose farsightedness during a basic eye examination. Your eye doctor will dilate (widen) your pupils. Pupils are the black circles in the center of your eyeballs. Your eye doctor will put drops in your eyes to do this. Then they’ll use a magnifying lens to look closely at your eyes. You might also need to look through various glass lenses to test your vision.
Farsightedness isn’t usually picked up in children’s vision tests at school. These tests generally involve reading charts of letters from across the room. This only detects nearsightedness, which is the inability to see things far away.
Hyperopia Treatment
Farsightedness can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses to change the way light rays bend into the eyes.
If your glasses or contact lens prescription begins with plus numbers, like +2.50, you are farsighted.
You may need to wear your glasses or contacts all the time or only when reading, working on a computer or doing other close-up work.
Refractive surgery, such as LASIK or CK, is another option for correcting hyperopia. Surgery may reduce or eliminate your need to wear glasses or contact lenses.
Frames and lenses for Hypermetropia.
At Eye-shop you can find a vast selection of designer frames and economic frames suitable for myopia . With every pais of frames you get FREE lenses with your prescription




 Farsightedness occurs when light entering the eye is focused behind the retina instead of directly on it . This is caused by an eye that is too short, whose cornea is not curved enough, or whose lens sits farther back in the eye than normal.
Farsightedness occurs when light entering the eye is focused behind the retina instead of directly on it . This is caused by an eye that is too short, whose cornea is not curved enough, or whose lens sits farther back in the eye than normal.
